What is DMSO?
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) was first discovered in late 19th century Germany as a byproduct of wood pulping. DMSO can also be found in fruits, in the sea, and in the atmosphere.
DMSO is a colorless, transparent, hygroscopic fluid over a wide range of temperatures. DMSO rose to fame due to its ability to easily pass through the skin and other biological membranes. It's a sulfur-based compound with some amazing healing properties.
Dimethyl Sulfoxide is derived from dimethyl sulfide, a by-product of the manufacture of paper. Dimethyl Sulfide is a naturally produced biogenic gas essential for the earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Sulfur is also an element of the earth and is essential to life. It is the eighth most prevalent element in the human body, not as sulfur itself but always in combination with other elements, most often, in complex molecules and, less often, in simple molecules such as DMSO.

DMSO is a powerful free radical scavenger and an effective anti-inflammatory agent. It also has pain-relieving, collagen-softening, and anti-inflammatory characteristics, making it an incredibly effective natural pain reliever.
DMSO was and is still used on racehorses and by veterinarians today. For humans, it's most commonly used to help relieve joint and arthritis pain.
DMSO is commercially available in the United States ranging from industrial grade (found in tractor and farm stores) and highly pure grade DMSO for drug delivery and health-care applications. Industrial Grade is commonly used on horses, and dogs whereas 99.99% Pure Pharmaceutical Grade DMSO is for human use.
Side effects of DMSO can be temporary local irritation of the skin and a potential taste and/or sometimes smell of garlic upon use.
DMSO Uses
People have been known to use DMSO to try to help with a plethora of issues including but not limited to:
- Inflammatory diseases
- Joint pain relief
- Cancer side-effects (pain)
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Headaches and Migraines
- Fibromyalgia
- Psoriasis
- Shingles
- Candida
- Eczema
- Tendonitis
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Amyloidosis
- Scleroderma
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Diabetic Neuropathy pain
- Varicose and Spider veins
- Burns and scar tissue
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- Furuncular otitis
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Hemorrhoids
- Muscle spasms
- Bursitis
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrom
- General stiffness and soreness
- To improve range of motion
"I can't tell you how much the DMSO has made a difference. I have arthritis in my lower back and hip. At times I can barely walk. DMSO has given me the ability to actually live a normal life."
- Jan B.

15 Major Therapeutic Properties of DMSO: Referenced from "DMSO, Nature's Healer" by Dr. Morgan Walker pages 50 and 152.
The most common use for DMSO is as a natural pain reliever.
Pain is the most common reason for people to seek medical help and is a major complaint in many medical conditions and disorders. It is common knowledge that acute or chronic pain can significantly interfere with a person’s quality of life and normal daily function.
"If joint and/or muscle pain is interfering with your quality of life, I suggest you give dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) a try.” - Dr. Julian Whitaker

So, why go natural?
Painkillers, particularly opioid drugs, are the leading cause of unintentional overdose deaths in teens and adults, and according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), such deaths have reached epidemic proportions in the United States. The number of unintentional drug poisoning deaths exceeds either motor vehicle accidents or suicides, two of the leading causes of death in the United States. One of the reasons for easily overdosing and dying from narcotics is their powerful action as central nervous system (CNS) depressants, especially when the narcotic is combined with alcohol or another pain medication.
DMSO is similar to aspirin in that it blocks the production of certain prostaglandins by controlling the on-off switch in cells that regulate pain and inflammation, among other things. That is likely the reason why aspirin stops mild inflammation and pain.
However, DMSO goes a step farther than aspirin in that it not only blocks the prostaglandins that can induce pain and inflammation but also stops or slows down conduction of pain fibers when it is administered topically.
Unlike aspirin and other popular painkillers, DMSO is not considered toxic to the stomach or gut where aspirin can cause peptic ulcers or gastrointestinal tract irritation at therapeutic doses.
Claim your bottle from Herbal Mana and experience DMSO for yourself.
What People Are Saying About
DMSO From Herbal Mana...
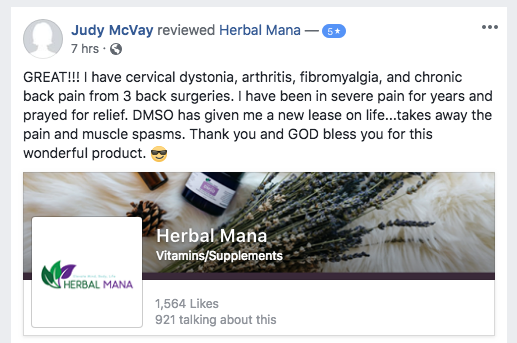


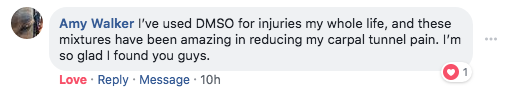
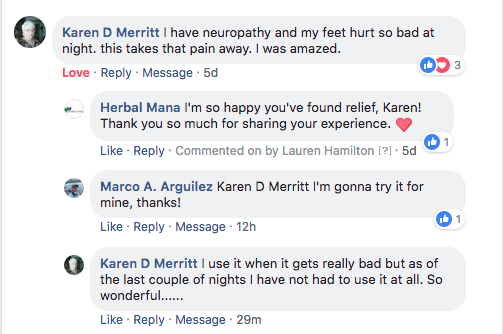
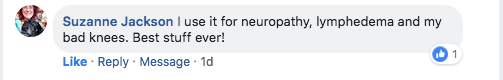
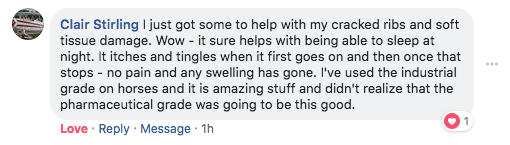

*The individuals providing testimonials in this report experienced extraordinary results while using this product. As individuals differ, so will results. They were not paid for their testimonies.
Herbal Mana, LLC © 2025.
All Rights Reserved
2007 W Silver Creek Dr, Nampa, ID 83686
Contact | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Health Disclaimer | Customer Service: support@herbalmana.com
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease. The individuals providing testimonials in this report experienced extraordinary results while using this product. As individuals differ, so will results. They were not paid for their testimonies.
References:
Jacob, Stanley Wallace, and Jack C. de la Torre. Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO) in Trauma and Disease. CRC Press, 2015.
“DMSO: Many Uses, Much Controversy.” Pharmacology of DMSO, Alternative & Complementary Therapies, www.dmso.org/articles/information/muir.htm.
Whitaker, Julian. “DMSO Treatment Relieves Joint & Muscle Pain.” Health Vitamins & Supplements Products, www.drwhitaker.com/dmso-treatment-relieves-joint-and-muscle-pain.
Oler, Dr. Chad. “The Difference between Sulfa (Drugs), Sulfites and Sulfur.” Natural Solutions, 25 May 2017, naturalsolutionsforahealthyyou.com/the-difference-between-sulfa-drugs-sulfites-and-sulfur/.
Dr. Walker, Morton. DMSO Nature's Healer. Avery, 1993.